The Value of RFID in Inventory Management & Supply Chain Visibility
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is revolutionizing inventory management and supply chain visibility. While barcodes have been the dominant tool for item identification for decades, RFID offers a powerful alternative with advantages like real-time tracking, non-line-of-sight reading, and faster automation. Although RFID implementation requires more planning and investment than barcoding, it can provide significant efficiency gains for businesses seeking to streamline operations and reduce errors.
Why RFID is Worth Considering
To determine if RFID is the right fit for your business, it’s important to evaluate your needs and operational challenges. Unlike barcodes, RFID does not require line-of-sight to read tags, which makes it ideal for tracking items moving through conveyor systems or stored in hard-to-see locations. The technology also supports varied read ranges, from a few inches to over 10 feet, depending on the tag and reader setup. RFID can be particularly effective when items are traveling at high speeds or are fixed at certain checkpoints.
However, environmental factors must be considered. Items containing metal or liquids can interfere with RFID signals, impacting system performance. Similarly, the choice of fixed or mobile readers depends on whether you need automated scanning at warehouse entry points or manual inventory checks on the move.
Types of RFID Technologies
RFID operates in three main frequency ranges. Low Frequency (LF) systems work well for close-contact applications like ID badges or access control, but their range is limited to a couple of inches. High Frequency (HF) systems can read tags up to 3 feet away, making them ideal for small item tracking and applications like healthcare equipment management.
For supply chain and inventory purposes, Ultra High Frequency (UHF) is the most widely adopted RFID solution. UHF systems offer extended read ranges of up to 10 feet, making them highly effective for item-level and container-level tracking. UHF’s affordability and flexibility have made it a popular choice for businesses looking to manage large volumes of inventory efficiently.
RFID tags are also classified as active or passive. Active RFID tags have their own battery power, enabling long-range and high-speed scanning, but they are costly and bulky. Passive tags, on the other hand, rely on the reader’s signal for power, making them thinner, more affordable, and ideal for product-level tracking in inventory systems.
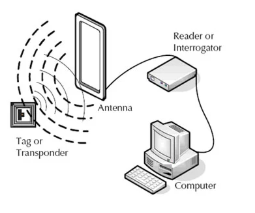
How RFID Works
A typical RFID system includes four key components: tags, antennas, readers, and host software. When a passive RFID tag enters the signal field of an antenna, the tag receives power from the reader. It then “backscatters” its stored data, which is captured by the antenna and processed by the host software. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags can be read even if they are not in direct view or perfectly oriented, enabling faster and more efficient inventory tracking.
The host software uses the captured data for applications such as asset tracking, inventory control, or logistics management. For example, fixed RFID readers can monitor inventory as it passes through warehouse doors, while mobile readers allow employees to conduct manual counts while on the move. Desktop RFID readers offer a plug-and-play option for situations that require reading tags next to a PC, such as retail checkouts or quality control stations.
Challenges and Limitations
While RFID is highly effective, it is not without limitations. Environmental factors such as metals and liquids can interfere with signals, reducing accuracy. Dense collections of items may also pose challenges, as tags in the center may not receive enough signal power to activate. These factors require extensive testing and system design to achieve optimal results.
Additionally, RFID systems involve higher upfront costs compared to barcode solutions. However, businesses that plan carefully and implement RFID effectively often achieve significant long-term savings through reduced errors, improved accuracy, and labor efficiency.
Components of an RFID System
An RFID system begins with the selection of the right tags, which are designed with a combination of chipsets and antennas to store and transmit data. The choice of tags depends on the environment, product type, and read requirements. For high-volume applications, RFID printers simplify the process by encoding tags and printing barcodes as a backup, ensuring data accessibility even if the RFID tag is damaged.
The RFID readers themselves come in various forms. Fixed readers are ideal for automated scanning at checkpoints, such as warehouse docks or conveyor lines. Mobile readers, which resemble handheld computers, are versatile tools for conducting inventory counts and asset tracking across facilities. Desktop readers, though limited in range, offer quick and easy data capture for localized applications.
Finally, middleware software ties the system together. Unlike barcode scanners, RFID readers do not output basic text data directly. Instead, middleware processes the RFID data and integrates it with inventory management or enterprise software. Systems supporting Low Level Reader Protocol (LLRP) ensure compatibility with most RFID readers.
The Benefits of RFID in Supply Chain Management
The greatest value of RFID lies in its ability to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and automation. It enables businesses to track inventory in real time without requiring manual scanning. By reading multiple tags simultaneously, RFID reduces the time and labor involved in inventory checks. Its non-line-of-sight capability allows for greater flexibility, especially in environments where items are stacked, moving, or difficult to access.
Conclusion
RFID technology is transforming the way businesses manage inventory and supply chains by offering faster, more accurate, and automated tracking solutions. While the technology presents challenges, such as signal interference and higher initial costs, the benefits far outweigh these limitations when implemented correctly.
For businesses exploring RFID, it is best to start with a small-scale pilot project, test its feasibility, and gradually scale up. With careful planning and the right resources, RFID can provide unparalleled visibility and efficiency in your inventory management processes, giving you a significant edge in a competitive market.
Revolutionizing Labeling: Latest Advances in Print-and-Apply Technology
Print-and-apply technology is transforming the way businesses handle labeling, offering unmatched efficiency and precision. By integrating a printer with an automated label applicator, this technology streamlines workflows by eliminating manual processes. No longer do employees need to print labels separately and load them into applicators or apply them manually. These all-in-one systems deliver consistent labeling with precise placement on products, envelopes, and packages, boosting productivity and accuracy.
Innovative Print-and-Apply Solutions for Diverse Industries
Today’s cutting-edge print-and-apply solutions are designed to meet the unique challenges of various industries. These advancements provide greater flexibility, speed, and precision to keep up with evolving operational demands.
Ecommerce: High-Speed Labeling for a Variety of Packages
Ecommerce companies must operate at lightning-fast speeds while maintaining accuracy to meet customer expectations. The diversity of package sizes—from slim mailers to oversized boxes—requires adaptable labeling solutions.
Modern print-and-apply machines accommodate a broad range of package sizes with innovative features like applicator tips with wider stroke ranges. These machines can label both flat mailers and tall boxes seamlessly on moving conveyors. Newer models use safer wheel-based designs instead of belts and rely on gravity for label application instead of air puffs, enhancing speed and throughput.
Precision Labeling: Enhanced Accuracy with AI Integration
For businesses where precision is critical, advanced systems ensure consistent labeling for items of the same size traveling on conveyors.
Many systems now incorporate AI-driven vision technology to verify label accuracy. These systems can check for correct serialization, expiration dates, and quality control, identifying and correcting issues like missing characters or damaged labels. The result? Near-perfect labeling accuracy for even the most sensitive use cases.
Automotive: Robotic Label Placement for Complex Surfaces
In industries like automotive, where interior labeling on engine or auto body parts is required, traditional labeling systems fall short. Print-and-apply solutions equipped with robotic arms provide the flexibility to label irregular surfaces or hard-to-reach areas with precision.
Robotic systems also excel at pallet labeling, offering extended reach to apply multiple labels to large, palletized items. Whether it’s the front, side, or both, these systems ensure proper labeling for streamlined operations.
Benefits of Barcodes, Inc Print-and-Apply Solutions
- Boosted Production Rates: Automating labeling and printing accelerates production lines, enabling higher output and efficiency.
- Lower Labor Costs: Automation minimizes manual labor, cutting expenses and optimizing resource allocation.
- Improved Accuracy: AI-driven inspections ensure error-free labeling, reducing costly mistakes and maintaining consistency.
- Unmatched Versatility: Systems handle a wide range of box sizes without manual adjustments, ideal for diverse packaging needs.
- Quality Assurance: Motorized guides deliver precise label placement, ensuring flawless results every time.
Find the Ideal Print-and-Apply System for Your Needs
At Barcodes, Inc. we provide a comprehensive range of automated labeling solutions tailored to your specific applications. Our vendor-neutral approach ensures you get the best system to meet your operational demands for speed, flexibility, and precision.
Take advantage of the latest advancements in print-and-apply technology to boost efficiency, handle diverse package sizes, and achieve robotic precision for interior labeling. Ready to optimize your labeling processes? Contact Barcodes, Inc. today to get started!
How Connected Packaging Powers the Circular Supply Chain
Connected packaging is revolutionizing supply chains, boosting efficiency, and driving sustainability. John Dwyer, Vice President of Digital Innovation at Smurfit WestRock, highlighted the transformative potential of Born-Digital packaging during a guest session hosted by Levata. Barcodes, Inc. is a Levata company.
By combining cutting-edge technologies like traceability, automation, and circular economy principles, Smurfit WestRock is redefining the role of packaging in modern business. Below is an overview of Dwyer’s insights and the impact of Born-Digital packaging on sustainability and supply chain efficiency.
Transforming Supply Chains with Connected Packaging
Traditional supply chains often face inefficiencies, including waste from overstocking. The pandemic exposed these vulnerabilities, emphasizing the need for smarter, connected solutions.
Smurfit WestRock’s Born-Digital packaging integrates advanced technologies like RFID, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), NFC, and serialized QR codes into packaging, creating digital identities for products. These innovations enable real-time tracking, improve inventory visibility, reduce waste, and optimize delivery timelines.
For instance, Smurfit WestRock collaborated with a quick-service restaurant chain to track fresh beef throughout its supply chain. By incorporating RFID technology into refrigerated packaging, the company ensured precise, scalable solutions for transitioning from frozen to fresh beef—an essential step for maintaining quality and meeting demand.
Driving Recycling and Sustainability
Sustainability is at the core of Smurfit WestRock’s operations. The company operates 32 recovery facilities in North America, collecting two-thirds of Walmart’s packaging waste and transforming it into new materials. This closed-loop system supports retailers’ ESG goals while reducing waste.
A standout example is Smurfit WestRock’s leadership in the pizza box market, producing approximately 3 billion boxes annually, covering 55% of the U.S. market. Domino’s has introduced QR codes on its boxes to educate customers about local recycling guidelines. Research conducted by Smurfit WestRock confirms that pizza boxes are recyclable, even with food residue, further reducing environmental impact.
Key Trends Shaping Born-Digital Packaging
Several key trends are driving the adoption of connected packaging:
- Real-Time Data Demand: Businesses require instant access to data for better decision-making, particularly in retail and logistics. Connected packaging improves inventory accuracy and supply chain visibility.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Innovations like Wi-Fi 6E and 5G ensure seamless data transfer in harsh environments.
- Circular Economy Integration: Businesses are prioritizing recyclable materials and digital traceability to minimize environmental footprints and meet regulatory standards.
Smurfit WestRock is leading the charge with advanced solutions like light-sensitive sensors that detect unauthorized package openings, enhancing security and trust. By creating scalable, end-to-end systems in partnership with companies like Barcodes, Inc. and SLS, the company ensures seamless integration of sensors, readers, and gateways to address complex supply chain challenges.
Maximizing ROI with Smart Packaging
Connected packaging offers businesses significant returns on investment, often within 12 months. Automating processes like cycle counting allows organizations to redeploy labor to higher-value tasks, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
For instance, smart packaging helps retailers avoid costly penalties for incomplete or late shipments by providing electronic proof of delivery.
A Vision for a Sustainable Future
John Dwyer concluded his presentation by reaffirming Smurfit WestRock’s dedication to the circular economy. Approximately 30% of old corrugated containers in the U.S. are recycled into new packaging, showcasing the company’s commitment to sustainability. As regulations like FSMA and EPR evolve, Smurfit WestRock’s ability to track and recycle packaging will remain a vital tool for achieving compliance and advancing sustainability.
Discover the Future of Packaging
By combining innovation, sustainability, and strategic partnerships, Smurfit WestRock is revolutionizing packaging and creating a smarter, more connected supply chain. Learn how your business can leverage connected technologies, recycling innovations, and sustainable practices to transform your operations and meet evolving market demands.
Contact us today to explore the power of Born-Digital packaging in driving a sustainable, circular economy.




